Invest in commercial real estate, with us.
Our experienced team brings accredited investors institutional quality, asset-backed alternative investment options.
View Opportunities Sign InOur track record.
How we are different.
We target asset-backed investments to deliver strong near-term cash flow and solid returns.
Simple, understandable and transparent. We provide dedicated service to our investors.
Growth markets with strong population trends, increasing household income and positive economic indicators.
Trusted, highly specialized operating partners, each with deep expertise in their asset category.

Experience Matters

We have invested more than $112 million in equity in the past five years.
We have deployed equity in 12 states, across 33 partnerships in 7 industry classes.
We have more than 50 years of private equity and real estate investing experience.
Diversified portfolios — less risk , less volatility.
Diversifying with private equity and real estate can help to protect you from volatility and risk, because its performance typically isn’t tied to the stock market.
We offer you the ability to diversify like the experts, giving you the power to invest in what fits your risk and return profile.

Best-in-class always — only the most exclusive opportunities.
SageStreet evaluates hundreds of deals a year. We execute a rigorous underwriting process on each investment, which includes extensive review of both the operating partners and assets in order to determine the best opportunities for our investors.

Institutional quality — asset-backed for long-term growth.
We focus on investments for which the cashflow stream is backed by a hard asset that always has intrinsic value. This mitigates risk by accelerating a portion of the return to the investor during the time we hold the asset.
Institutional investors have had access to these types of assets for years, now you do too.

Passive income — real assets, real returns.
Real cash returns both from quarterly distributions and the sale of the asset.
We enable our investors to create a diversified portfolio of yield-producing assets without the active management and stress associated with owning private equity and real estate directly.

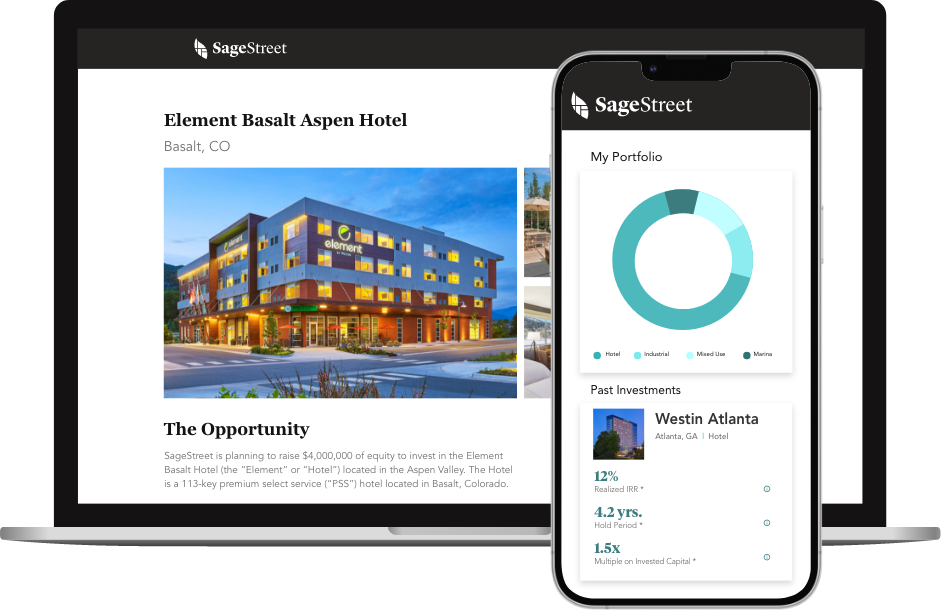
Create your financial legacy.
Our best-in-class investment platform brings targeted investment deals to our accredited investor community, providing you the freedom to build the future you imagine.
Our dedicated team is with you through the entire process. Any question, any time.
Get Started